The Uninterruptible Power Supply: Ensuring Continuous Power in a Digital World
In today’s technology-driven world, the continuity of electrical power is critical for both businesses and homes. Sudden power outages can lead to data loss, hardware damage, and significant financial losses. This is where the uninterruptible power supply (UPS) becomes an essential component of any electrical system. But what exactly is a UPS, and how does it safeguard your devices and systems? Let’s explore its features, benefits, and practical applications.
What is the Uninterruptible Power Supply?
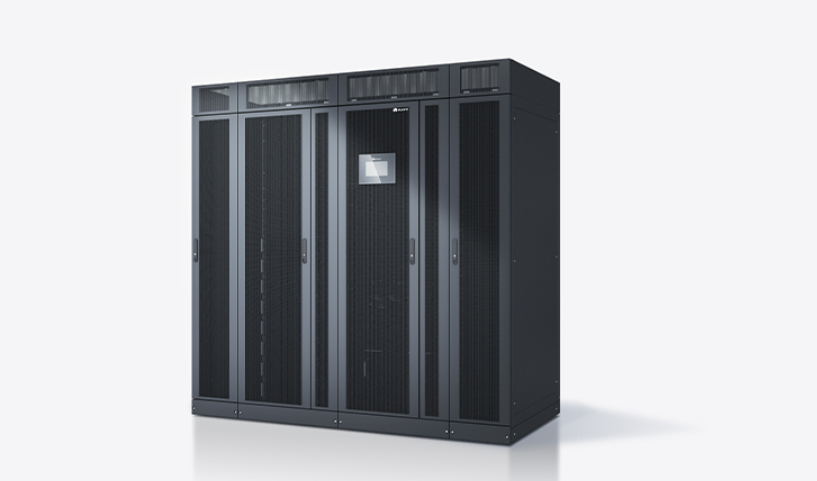
An uninterruptible power supply is a device that provides emergency power to connected equipment when the main power source fails. Unlike a conventional backup generator, a UPS delivers immediate power without any delay, ensuring that sensitive electronics, such as computers, servers, and medical devices, remain operational during a power disruption.
At its core, a UPS consists of three main components: a battery, an inverter, and a charging system. The battery stores energy, the inverter converts stored energy from DC to AC, and the charging system ensures the battery remains fully charged during normal operation.
See also: Operational Strategy Review 9055686970, 645492658, 6971941419, 4075830846, 3301007477, 659487443
Types of Uninterruptible Power Supplies
Understanding the different types of UPS is crucial for selecting the right system for your needs. There are three primary categories:
- Offline/Standby UPS
This is the most basic type of UPS. It remains inactive until a power failure occurs, at which point it switches to battery power. It is cost-effective and suitable for home computers or small office setups. - Line-Interactive UPS
This UPS provides voltage regulation by automatically adjusting low or high voltages without switching to battery power. It is ideal for environments with frequent minor power fluctuations. - Online/Double-Conversion UPS
The online UPS offers the highest level of protection by continuously converting incoming AC power to DC and then back to AC. This ensures a consistent and clean power supply, making it suitable for data centers, hospitals, and mission-critical applications.
Benefits of Using a UPS
Implementing an uninterruptible power supply offers numerous advantages:
- Prevents Data Loss: Sudden power outages can corrupt files or crash systems. A UPS allows safe shutdown and data preservation.
- Protects Equipment: Voltage spikes, sags, and outages can damage electronic components. A UPS stabilizes voltage and prevents such damage.
- Maintains Productivity: Businesses can continue operations during short-term outages without interruption.
- Supports Critical Infrastructure: Hospitals, emergency response centers, and data centers rely on UPS systems to maintain continuous operations.
- Reduces Downtime Costs: For businesses, downtime can result in significant financial loss. UPS systems mitigate this risk.
How to Choose the Right UPS
Selecting the appropriate UPS depends on several factors:
- Power Requirements: Calculate the total wattage of devices that need protection.
- Runtime: Determine how long you need the UPS to provide backup power during an outage.
- Type of UPS: Consider the nature of your power environment to choose between standby, line-interactive, or online UPS.
- Additional Features: Some UPS systems offer surge protection, automatic voltage regulation, and remote management.
Maintenance and Best Practices
Proper maintenance ensures that your UPS functions reliably:
- Regularly check the battery health and replace it as needed.
- Keep the UPS in a cool, dry environment to prevent overheating.
- Perform periodic self-tests if your UPS supports this feature.
- Avoid overloading the UPS beyond its rated capacity.
Applications of the Uninterruptible Power Supply
The UPS is widely used across various sectors:
- IT and Data Centers: Protects servers, network devices, and critical applications.
- Healthcare: Ensures medical equipment remains operational during power disruptions.
- Home Offices: Keeps personal computers and networking equipment safe.
- Industrial Automation: Maintains continuous operation of sensitive machinery.
- Telecommunication: Ensures uninterrupted communication services.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: How long can a UPS provide power?
A UPS provides backup power based on its battery capacity. Small units may last 5–15 minutes, while large systems can operate for several hours.
Q2: Can a UPS replace a generator?
No. A UPS is ideal for short-term power interruptions, while generators are better suited for long-duration outages.
Q3: Does a UPS consume electricity while idle?
Yes, UPS units draw a small amount of power to keep the battery charged and ready.
Q4: How often should UPS batteries be replaced?
Typically, UPS batteries last 3–5 years, but this depends on usage, temperature, and load.
Q5: Can multiple UPS units be connected together?
Yes, in large-scale setups like data centers, multiple UPS units can be connected for redundancy and extended capacity.
Conclusion
In a world increasingly dependent on continuous power, the uninterruptible power supply plays a crucial role in protecting data, equipment, and productivity. From home offices to large industrial and healthcare facilities, the UPS ensures that operations continue smoothly even during unexpected outages. By understanding the types, benefits, and maintenance practices of UPS systems, you can make an informed decision to safeguard your electronics and maintain uninterrupted power supply when it matters most.